Currently Empty: 0.00zł
Where Is A Notes Receivable Reported In The Balance Sheet?

Notes arising from loans usually identify collateral security in the form of assets of the borrower that the lender can seize if the note is not paid at the maturity date. You should classify a note receivable in the balance sheet as a current asset if it is due within 12 months or as non-current (i.e., long-term) if it is due in more than 12 months. These loans are typically short term, due to be repaid to the business within one year. In this case, the current asset account Note Receivable is used to keep track of amounts that are owed to the business.

What is the journal entry for interest on a note receivable?
Proper management can ensure that your business has enough cash on hand to meet its financial obligations and invest in growth opportunities. Another benefit is that Notes Receivable typically offer higher interest rates than other forms of financing, such as bank loans or lines of credit. This means companies can earn more money on their investments in these notes. If the note receivable is due within a year, it’s treated as a current asset, treated as non-current assets. The amount debited to notes receivable represent the interest earned in month of December on the carrying amount at the end of November because the note carries compound interest.

3.2 Maturity (Due) Date
The Interest Receivable amount of $124 is reducing the Interest Receivable account to show that the interest has been paid. Note Receivable amount represents the payment in full for the Note Receivable. It has a stronger legal claim than Accounts Receivable, meaning it is more likely to get paid than Accounts Receivable if the maker enters bankruptcy.
- Notes can also be used for sales of property, plant, and equipment or for exchanges of long-term assets.
- The terms of the note specify that the loan must be repaid in full within one year.
- These notes usually come with interest and principal payments due over time, making them similar to loans.
- 11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements.
- Since the note is void but the customer did not pay or make arrangements for a new note, the only account remaining to record what is owed is Accounts Receivable.
- Accruing tax liabilities in accounting involves recognizing and recording taxes that a company owes but has not yet paid.
Interest Rate Calculation on Notes Receivable

If Anchor used ASPE, there would be a choice between the effective interest method and the straight-line method. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly. In other cases, a customer’s credit rating may cause the seller to insist on a written note rather than relying on an open account. A case in point is the sale of equipment or other personal or real property in which payment terms are normally longer than is customary for an open account. Notes receivable refers to a written, unconditional promise made by retained earnings balance sheet an individual or business to pay a definite amount at a definite date or on demand.
Our Services
Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise. Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible. Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications.
- Simply put, they’re written promises from customers or other entities to pay back the company at a later date.
- The accounts receivable is just as valid a claim as are the notes receivable, as well as the interest.
- The accounting treatment of interest that is accrued but remains unpaid up to balance sheet date, depends on whether the interest is compound or simple.
- This balance represents 89 days 30 days in January, 28 days in February, 31 days in March of the the 90 day note.
- Just like accounts receivable, notes receivable is a balance sheet asset account.

Promissory notes are a written promise to pay cash to another party on or before a specified future date. The effective interest rate is the rate that exactly discounts the expected stream of future cash payments through the life of the note receivable to the net carrying amount of the financial asset. This method captures the financial reality of the transaction more accurately than the straight-line method, which would allocate the same amount of interest income to each period regardless of the actual passage of time. The effective interest rate takes into account the impact of compounding, providing a more precise measure of the return on investment for the lender. The straight-line method is easier to apply but its are notes receivable a current asset shortcoming is that the interest rate (yield) for the note is not held constant at the 12% market rate as is the case when the effective interest method is used. This is because the amortization of the discount is in equal amounts and does not take into consideration what the carrying amount of the note was at any given period of time.
- Notes receivables describe promissory notes that represent loans paid from a company or business to another party.
- If a company is selling to its customer and issuing a Note Receivable rather than an Accounts Receivable, a Revenue account would be credited to record the revenue.
- Notes receivables are the written promises that state the date when the amount will be paid to the creditors (Companies who sell goods on credit) by the debtor (Customers who purchase goods on credit).
- If the note receivable is due within a year, it’s treated as a current asset, treated as non-current assets.
- The disclosures also encompass information about the credit quality of notes receivable, including the credit risk profile and any changes in the risk during the reporting period.
- Notes receivable are classified as current assets when the repayment period is within one year.
It’s important for businesses to properly classify their notes receivable since it affects financial reporting and analysis. Failure to accurately classify these assets could result in misrepresenting the company’s liquidity position and profitability. Current notes receivable are expected to be collected within a year, while non-current notes receivable have longer maturities. Notes receivable are classified as either current assets or non-current assets depending on when they are expected to be repaid. If repayment is due within one year (or the operating cycle of https://www.bookstime.com/ the business), they’re considered current assets; otherwise, they fall into the non-current category. Cash or bank is debited by the sum of principal amount and interest not yet received.
Written by True Tamplin, BSc, CEPF®
Set your business up for success with our free small business tax calculator. Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI’s full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs. CFI is the global institution behind the financial modeling and valuation analyst FMVA® Designation. CFI is on a mission to enable anyone to be a great financial analyst and have a great career path. In order to help you advance your career, CFI has compiled many resources to assist you along the path.
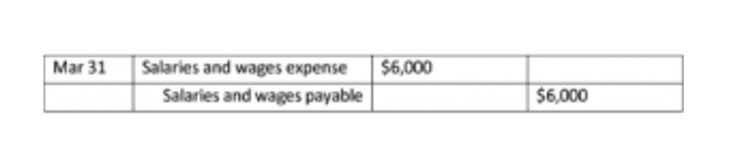
A note receivable will mention the two parties involved, the payee and the payer. Notes receivable can be an important component of a company’s financial health – but it’s important to manage them carefully and keep track of all repayments and interest accruals. When interest will be paid on a Note Receivable is specified in the promissory note. Or, it may specify that interest will be due at certain points during the note’s duration (monthly, quarterly, semi-annually).

